Storage Costs
Masthead collects and analyzes BigQuery resource metadata and usage logs to estimate the cost for the data assets and shows the recommendations to optimize the spending.
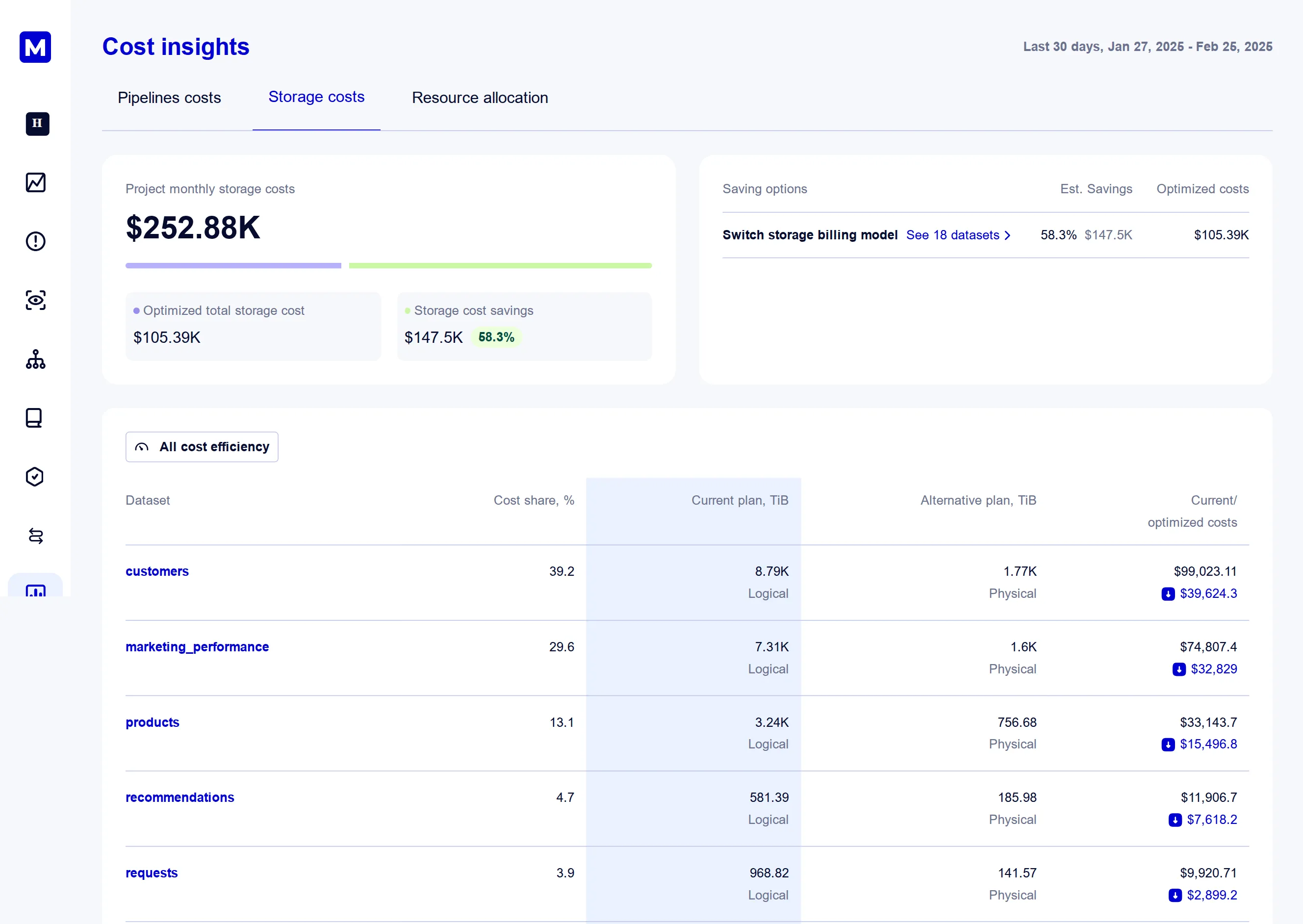
Storage Cost Insights page shows the details of the aggregated estimated metrics per dataset:
- storage size - most recent data point,
- storage cost - estimation based on the data storage usage over the last 30 days.
Masthead analyses each of these parameters and offers a set of recommendations optimizing the total storage bill.
Recommendations
Alternative Billing Model for Dataset
BigQuery provides different storage billing models (Logical and Physical) that offer the flexibility in selecting the costs based on the data properties and operation patterns. Masthead analyzes the datasets metadata and the storage usage to estimate the optimal cost for each billing model.
Google Cloud Billing calculates the storage cost in the following way:
- logical storage cost:
active_logical_storage_size * active_logical_storage_price + long_term_logical_storage_size * long_term_logical_storage_price- or physical storage cost:
(active_physical_storage_size + time_travel_physical_storage_size + fail_safe_physical_storage_size) * active_physical_storage_price + long_term_physical_storage_size * long_term_physical_storage_priceMasthead analyses your data storage usage retrospectively, and with the information about alternative costs of each of the billing model creates a recommendation for the opportunities where the switch will provide consistent and confident saving outcome.
Recommendation
- Review storage billing recommendations for the datasets on Storage Cost Insights page.
- Update storage billing model for a dataset to the recommended storage billing model.
The dataset configuration can be adjusted by running DDL statement:
ALTER SCHEMA PROJECT.DATASET SET OPTIONS( storage_billing_model = LOGICAL or PHYSICAL);DECLARE project_id STRING DEFAULT 'PROJECT';DECLARE dataset_names ARRAY<STRING>;
SET dataset_names = [ 'DATASET1', 'DATASET2'];
FOR dataset IN (SELECT name FROM UNNEST(dataset_names) AS name) DO EXECUTE IMMEDIATE FORMAT(""" ALTER SCHEMA `%s.%s` SET OPTIONS(storage_billing_model = 'LOGICAL/PHYSICAL'""", project_id, dataset.name);END FOR;Dead-end tables
By analyzing BigQuery lineage end-to-end Masthead identifies the tables that are being regularly updated, but have no downstream consumption.
The Dead-end label can be applied to the following resources:
- the regularly updated tables that don’t have downstream consumption during last 30 days (default period),
- pipelines that update them (see Dead-end pipelines)
- other upstream tables and pipelines that contribute solely to this process.
You can explore complete lineage with Dead-end labels by opening a Lineage page for a corresponding table or pipeline.
Recommendation
- review the tables labeled as
Dead-end(the complete list is available on the Dictionary page), - optimize the table updates to resemble the data consumption requirements,
- delete the tables when the are no clear consumers for the data.
Unused tables
Masthead helps you to track the costs related to the data assets that are not being actively used by labeling such tables as Unused . Based on your lineage these tables don’t have upstream or downstream consumption during last 30 days (default period).
Recommendation
- review the tables labeled as
Unused(the complete list is available on the Dictionary page), - delete unused tables to save on storage costs.
Limitations
- Dead-end and Unused labels are based on the lineage and usage patterns observed during the configured lookback window (30 days by default). Tables that are used less frequently will be labeled as unused.
- Some tables marked as “unused” or “dead-end” may be accessed through the following known methods not visible to Masthead’s monitoring: